Cervical Cancer is a cancer that begins in the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that joins the vagina. However, this type is the most common type of cancer in women. Cancer of the cervix occurs when healthy cells of the cervix mutate in their DNA. They grow, multiply and accumulate to form a mass or what is better known as a tumor. However, these cells can easily spread to nearby tissues if not discovered early and treated. Cervical cancer is easily treated and cure-able if noted early and proper treatment is given.
Types of cervical cancer.
So, a type is determined by the cell it attacks on the cervix, which also helps determine the course and treatment of the cancer.
- Squamous cell carcinoma– starts on the squamous cell which lines the outer part of the cervix. Cells are usually thin and flat.
- Adenocarcinoma – attacks the column-shaped glandular cells which line the cervix canal.
Rarely does squamous carcinoma occurs- it features both the squamous carcinoma and adenocarcinoma cells.
Causes of Cervical Cancer
So, the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the known common cause of cervical cancer. There are screening tests that can detect cervical cancer and precancerous calls. They include:
- Pap smear test- cells of the cervix are scraped and brushed then examined for any abnormalities.
- HPV DNA test – tests cells collected from the cervix.
Risk factors for cervical cancer.
- Family history.
- Sexual partners- a high number of sexual partners puts one at a greater risk of acquiring HPV.
- Weak immune system.
- Smoking.
- Miscarriage prevention drug exposure.
- Presence of other sexually transmitted infections for instance HIV and AIDS or gonorrhea.
- Having sex intercourse at an early age.
Symptoms.
Symptoms of early stages are:
- Pelvic pain during sexual intercourse.
- Waterly vaginal discharge that has odor.
- in addition, after menopause, one may have vaginal bleeding.
- Prolonged, heavy menstrual periods.
Symptoms of advanced cervical cancer.
- Pain and difficulty when passing urine.
- Painful bowel movements may lead to bleeding from the rectum.
- Backache.
- Additionally, swelling of the legs occurs.
Prevention measures.
- Vaccination- Young girls from the age of 9-15 years who have never engaged in sexual activity are given a HPV vaccine.
- Use of protection e.g. condoms when engaging in sexual intercourse, protects one from acquiring sexually transmitted diseases.
- Having one sexual partner.
- Avoid the use of tobacco products e.g. smoking.
- Also, regular pap smear testing.
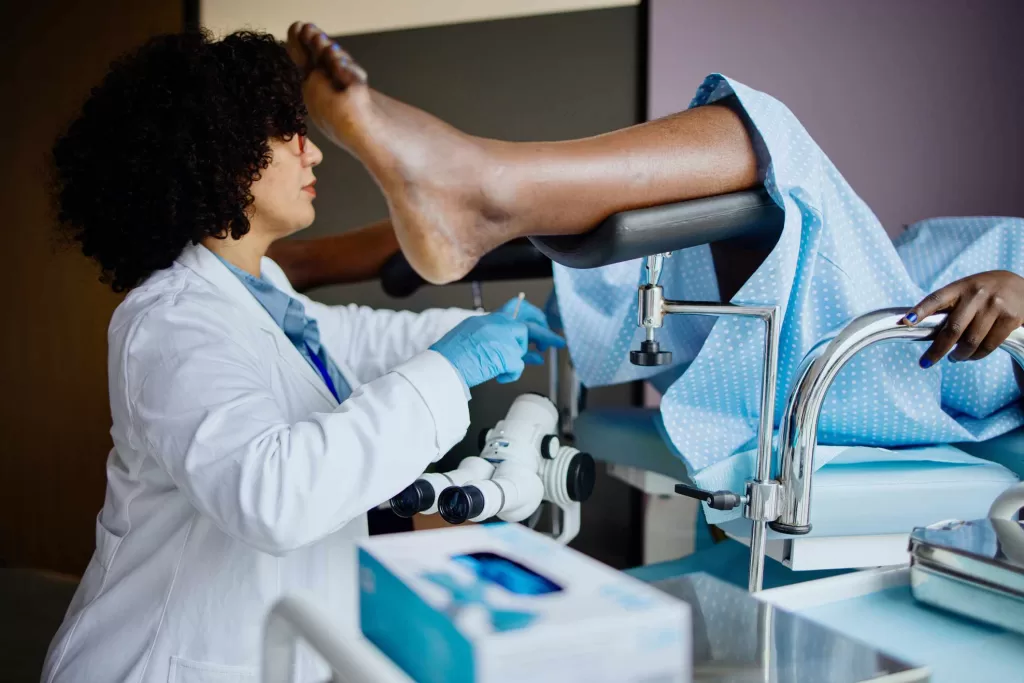
Diagnosis.
- Physical examination- a colposcope is used to examine for any abnormal cells in the cervix.
- Blood tests- complete blood count to check the number of red, and white blood cells, platelets, and the level of hemoglobin. Other tests that can be done are liver function tests, uric acid creatinine e.t.c
- Biopsy- can either be a punch or endo-cervical curettage biopsy. In punch biopsy, a sharp tool is used to pinch off small samples of the cervical tissues while in endocervical curettage a thin brush is used to scrape tissue samples from the cervix.
- Electrical wire loop- using local anesthesia a low-voltage electrical wire is used to obtain tissue samples.
- Con biopsy which is also known as conization- the deeper layer of the cervical cells is obtained.Done in hospitals under general anesthesia.
- Use of imaging tests like ultrasound and MRI.
Treatment.
Treatment depends on the extent or stage of the cancer. There are a number of tests that can be done to determine the stage of cancer. Include:
- Jane Lonsdale bio-age, KTBC-TV, children, husband, net worth.
- Danielle Ballard Death, Height, Accident, Wife, Family, Net Worth
- Raila Amolo Odinga Bio-age, family, career.
- William Kabogo Bio, Age, Education, net worth.
- Olivia Flowers Bio-Southern Charm, Children, Age, Husband.
- Uhuru Kenyatta biography, presidency net worth.
- Len Goodman Bio, Education, Career, Family, Net Worth
- Imaging tests like X-rays, CTs, and MRIs. Helps to determine if the cancer has spread to other tissues.
- Examination of the bladder and rectum visually.
Treatment for cervical cancer are:
- Surgery – early stages can be treated by use of surgery although it depends on the size of the tumor and future plans of having children. Its dividend is into three;
- Surgery to remove only the affected areas.
- Hysterectomy where both the cervix and uterus are removed. One can not have children in the future.
- Trachelectomy– only part of the cervix and affected areas is removed.
- Radiation therapy– uses high-powered energy beams like X-rays to kill cancer cells. Also used after surgery if the risk of cancer reoccurring is high. Not advisable for females who would like to be mothers in the future as it can cause menopause.
- Chemotherapy– uses chemicals to kill cancer cells. Given either through the vein or as a pill.
- Target therapy- focuses on blocking specific weaknesses in the cancer cells thus killing them.
- Immunotherapy treatment– helps the immune system fight cancer cells. Considered when the cancer stage is advanced and other treatment methods have not worked.
- Supportive care– is also known as palliative care. Focuses on giving relief from pain and other symptoms of the illness.
- List of Accredited Private Universities in Kenya
- What is the history of Kenyatta University?
- Bay head elementary school history, enrolment, programs offered.
- Egerton university, fees, location, courses.
- The best private primary schools in Nyeri county.
- Public Universities in Kenya
- List of best private primary schools in Kirinyaga County.