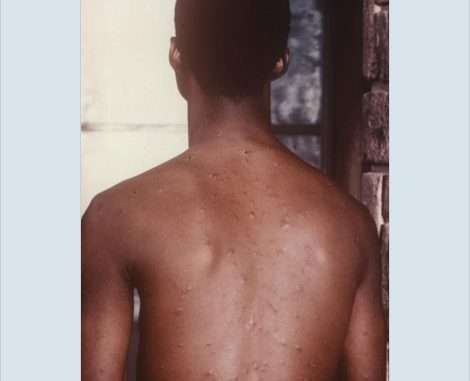
Chickenpox infection is an infection caused by the Varicella-zoster virus. However, It causes an itchy rash with small, fluid-filled blisters. Over several days, the blisters pop and start to leak. Therefore, it is highly contagious to people who haven’t had the disease or been vaccinated against it. The vaccine is available to protect children against chickenpox. The chickenpox vaccine is a safe, effective way to prevent it. Once you have had the illness you won’t catch it again from another person. Then they crust and scab over before finally healing.
Causes.
Chickenpox infection is caused by the Varicella-zoster virus. It spread through direct contact with the rash. However, it can also spread when a person with the illness coughs or sneezes and inhale the air droplets.
Complications.
Chickenpox is normally a mild disease. However, it can lead to complications which include:
- Bacterial infections of the skin.
- Dehydration.
- Pneumonia.
- Inflammation of the brain.
- Toxic shocks syndrome.
- Death.
Symptoms of chickenpox.
- Fever.
- Feeling tired.
- Headache.
- Skin rash.
- Scabs after the blisters break.
- Skin that looks blotchy.
- Spots that fade away.
- Stomachache.
- Bumps filled with a liquid that looks like milk water.
Stages of chickenpox.
It develops in stages. Before the rash appears, there may be:
An itchy rash will present on the face or body. However, the rash will formulate into spots. In addition, the severity of the rash can vary. The rash will develop into a fluid-filled blister that will turn cloudy. Therefore, these blisters make 3-5 days to hear. The blisters will become scabs. In addition, the scabs will fall off after about a week.
Treatment.
Chickenpox can be prevented by a vaccine. Treatment usually involves relieving indications, although high-risk groups may receive antiviral medication. In addition, a cool bath with baking soda, aluminum acetate help to treat chickenpox. Also, avoid scratching as it can cause scarring, slow healing, and increase the risk that the sores will become infected. However, doctors can prescribe antihistamines to relieve itching.
- Bay head elementary school history, enrolment, programs offered.
- Public Universities in Kenya
- Mount Kenya University history, fees, courses
- Best Public High Schools in Kiambu County.
- Egerton university, fees, location, courses.
- Kenya Institute of special education, courses.
- The best private primary schools in Nyeri county.