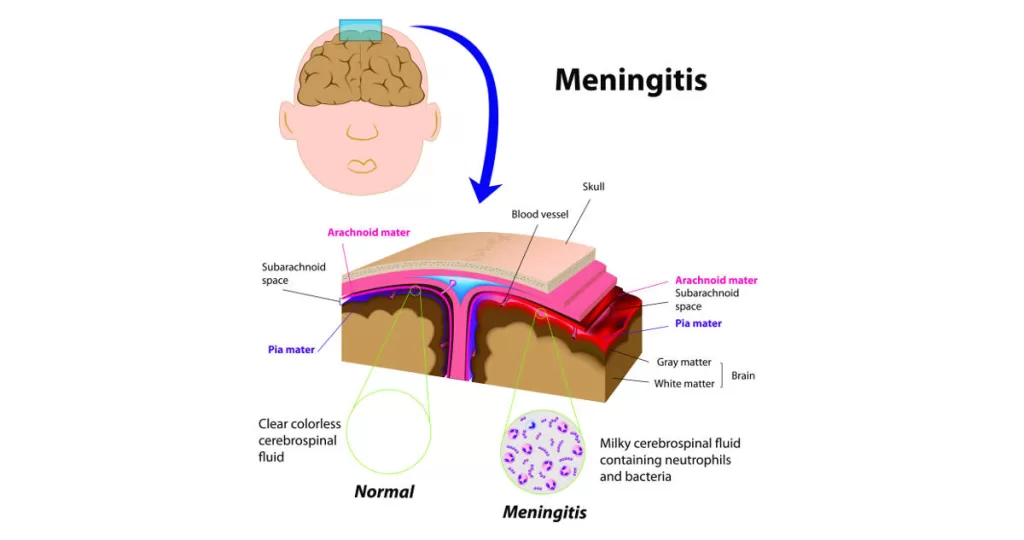
Meningitis is the inflammation of the meninges. This affects the protective membranes of the brain and the spinal cord. Depending on the causing agent, some can be spread from one person to the next through contact, sneezing, or kissing with those that are infected. It may be viral, fungal, or bacterial.
Causes
- Bacteria – They cause life-threatening meningitis that can lead to death within days if a proper antibiotic is not given. Delay treatment increases the risk of one having permanent brain damage. It may be due to blood infection, ear or sinus infection There are several strains of bacteria that causes meningitis. Include:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae. This is the most common cause of bacterium meningitis in infants and young children.
- Neisseria – it commonly causes upper respiratory infection but can also cause meningococcal meningitis when it enters the bloodstream. It is a highly contagious infection that can cause an epidemic in schools and military bases if not treated.
- Haemophilus influenza.
- Listeria monocytogenes. It is found in unpasteurized cheeses, hot dogs, and lunch meat. More susceptible to people who have low body immunity e.g. Pregnant women.
2. Viral e.g. enteroviruses like herpes simplex virus and mumps virus.
3. Fungal- contracted when one breathes in fungal spores in the soil, bird droppings, or decaying wood.
4. Parasitic meningitis causes eosinophilic meningitis. Occurs when parasite infections like tapeworms reach the brain.
5. Chemical reactions.
6. Drug allergies.
Symptoms of meningitis.
So, the symptoms in newborns and infants are:
- Jeff Eliasoph bio-wiki, age, children, wife, WVTM 13, net worth.
- Tasmin Mahfuz Bio, Wiki, DC News Now, Age, Education, Family, Children, Husband, Net Worth, and Career
- Travis Kelce age, education, wife, children, height, weight.
- Amy Adams age, husband, children, movies, illness, net worth
- David Robinett Bio, Wiki, KTAB News, Age, Education, Family, Children, Wife, Net Worth, and Career
- Gaston Glock age, family, wife, children, death, net worth.
- Dawn Stevens bio-age, children, husband, net worth, KMSP-TV.
- Poor feeding.
- High fever.
- Being sleepy.
- Vomiting.
- Sluggish.
- Constant crying.
- A bulge in the soft spot on the baby’s head.
- Stiffness of the body and neck.
In addition, in people from 2 years of age:
- Seizers.
- High fever.
- Nausea.
- Stiff neck.
- Confusion.
- Sensitivity to light.
- Painful headaches.
- Sleepiness.
Risk factor for meningitis.
- Age.
- Vaccination.
- Community setting.
- Pregnancy.
- Weak immune system.
Complication.
The longer one has an infection without treatment the more severe the complication. Complications include:
- Loss of hearing.
- Memory loss.
- Brain damage.
- Seizures.
- Kidney failure.
- Shock.
- Death.
Prevention of meningitis.
- Good hygiene practices like washing hands.
- Vaccination.
Diagnosis.
- Blood cultures.
- Imaging exams e.g. CT scan and MRI scan.
- Spinal tap.
Treatment.
- Intravenous antibiotics.
- Bed rest.
- Use of corticosteroid medication.
- Use of antiviral medication.
- Use of antifungal medication.
- List of Accredited Private Universities in Kenya
- Kenya Medical Training College, courses, requirements.
- Public Universities in Kenya
- Egerton university, fees, location, courses.
- List of Best private secondary schools in Nairobi County.
- Kenya Institute of special education, courses.
- How is The Lenana Boy school and location?