Urinary incontinence is a condition where one has no control of the bladder. However, it can be leaking of urine when one cough, sneezes, or has a sudden urge to pass urine that is so strong.
Types.
- Urge incontinence- This is a sudden, intense urge to pass urine that is followed by an involuntary loss of urine. Caused by infection, diabetes, or neurological disorder.
- Overflow incontinence- constant dribbling of urine due to incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- Functional incontinence- This is a mental or physical impairment that prevents one from making it in time to use the toilet.
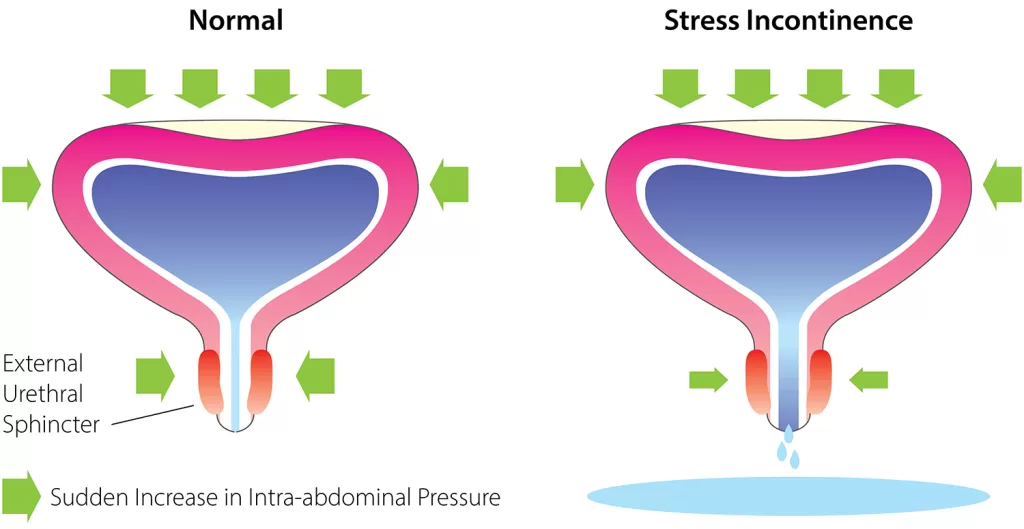
- Stress incontinence- So, when one coughs or sneezes pressure is exerted on the bladder leading to the leaking of urine.
- Mixed incontinence- However, this is a combination of stress incontinence and urge incontinence.
Causes of Urinary Incontinence
Are divided into two
1. Temporary urinary incontinence
Food, drinks, and medication can act as diuretics where they stimulate the bladder. Thin in turn increases the volume of urine. They include;
- Caffeine.
- Chilli peppers.
- Heart and pressure drugs.
- Alcohol.
- Chocolate.
- Large doses of vitamin C.
- Spicy foods.
Urinary tract infection which causes irritation to the bladder.
Constipation. The rectum is located near the bladder, both share many nerves. This can overact leading to urinary frequency when compacted stool exerts pressure on the nerves.
2. Persistent urinary incontinence
From underlying physical problems or changes. These include:
- Pregnancy- the increased weight of the fetus leads to pressure being exerted on the bladder.
- Childbirth- vaginal delivery weaken muscles of the bladder, leading to the dropping of the pelvic floor.
- Age- As one ages the capacity of the bladder to store urine decreases.
- Menopause- estrogen produced helps to keep the lining of the bladder and urethra healthy. A decrease in its level can lead to incontinence.
- Prostrate cancer- side effects of prostate cancer treatment can lead to incontinence.
- Enlargement of the prostate.
- Obstruction e.g. kidney stones can cause leakages.
- Neurological disorders e.g. brain tumors, or spinal injury can interfere with nerve signals in the bladder.
Risk factors of Urinary incontinence
- Gender- women are at a higher risk than men due to childbirth and pregnancy.
- Age.
- Body weight. Being obese/overweight increases pressure on the bladder making it weak.
- Smoking.
- Family history.
- Diseases e.g. neurological diseases.
Complications
- It can affect negatively one’s social, work, and personal life.
- Increase in urinary tract infections.
- Development of skin problems e.g. rashes and sores.
Prevention of Urinary incontinence
- Maintaining a healthy body weight.
- Not consuming bladder irritants like alcohol and caffeine.
- No smoking.
- Eating a diet that has fiber prevents constipation.
- Carrying out exercises that engage the pelvic floor muscles.
Diagnosis.
- Medical history report.
- Physical examination.
- Urinalysis- urine sample is tested for abnormalities and the presence of infection.
- Bladder diary- However, the amount of fluid taken, urine produced, number of incontinence episodes if any, and any urge to urinate experiences are recorded for a period of time.
- Pastvoid residual measurement. Urinate into a container, which is used to measure the amount produced. The amount of urine left in the bladder is checked using an ultrasound or a catheter. The amount of urine left in the bladder determines if there is a problem.
Treatment.
1. Behavioral techniques.
- Double voiding- one passes urine, and waits a few minutes before urinating again. Helps one to pass urine completely to avoid overflow.
- Bladder training- one delay to urinate for some minutes. This lengthens the time between trips to the toilet.
- Schedule toilet trips.
- Management of fluid and diet- avoid alcohol, acidic foods, or caffeine drinks. Loose weight and increasing physical activities.
2. Pelvic floor muscle exercises
. Are effective for stress incontinence as they help strengthen the pelvic muscles. Done with the assistance of a pelvic floor physical therapist.
- Bob Huggins bio-age, wife, children, attack, net worth.
- Who is Andrew Lincoln age, wife, children, career, net worth?
- Vanessa Welch bio-age, children, family, net, career.
- Kamala Harris age, education, husband, children, career, net worth.
- Bruce Bilson age, early life, education, wife, children, career.
- Ashley Johnson bio, Age, family, career, net worth.
- Walter Perez Bio, Age, Education, Height, Wife, Children.
3. Medication
This may include;
- Mirabegron-So, it relaxes the bladder muscles, and increases the amount of urine the bladder can hold and the amount of urine one passes. Helps to empty the bladder completely.
- Anticholinergics- e.g. trospium chloride, darifenacin, etc. Can calm an overactive bladder.
- Alpha blockers- e.g daxazosin,alfuzosin,silodasin e.t.c. In men, it makes the bladder muscle fibers in the prostate and the neck muscle relax. This makes it easy to empty the bladder.
- Topical estrogen- So, this helps to rejuvenate tissues in the urethra and vaginal areas.
4. Electrical stimulation
Gentle electrical stimulation can be used to treat urge incontinence and stress incontinence. The vagina or the rectum is stimulated and strengthing the pelvic floor muscles by temporarily inserting electrodes.
5. Medical devices.
- Pessary- Supports the urethra to prevent urine leakage. A flexible silicone ring is inserted into the vagina.
- Urethral insert- Before a specific activity e.g. playing tennis, a tampon-like device is inserted into the urethra. Acts as a plug to prevent leakages. It is removed before passing urine as it is disposable.
6. Interventional therapies.
- Nerve stimulators- use painless electrical pulses t stimulate the nerves that control the bladder. Are two types, one is implanted on the buttocks under the skin. Using wires it’s connected to the lower back. The other type is a removable plug which is inserted into the vagina.
- Botox injections can be helpful to people who have an overactive bladder.
- Bulking material injections- Help to keep the urethra closed and reduce leakage of urine. Synthetic material is injected into tissues of the urethra.
7. Surgery
- Sling procedure- strips of the body tissues are used to create a pelvic sling underneath the urethra and muscles of the bladder neck. Helps to keep the urethra closed when one coughs or sneezes. Use to treat stress incontinence.
- Prolapse surgery- A combination of prolapse surgery and sling procedures. Used to treat women who have pelvic organ prolapse and mixed incontinence.
- Bladder neck suspension- Done to give support to the urethra and bladder neck muscles.
- Artificial urinary sphincter – A small fluid-filled ring is implanted around the bladder neck. Keeps the urinary sphincter shut, till there is the urge to urinate. To urinate, a valve implanted under the skin is pressed causing the ring to deflate thus allowing urine to flow.
8. Use absorbent pads and catheters.
- The best private primary schools in Nyeri county.
- How is The Lenana Boy school and location?
- Kenya Medical Training College, courses, requirements.
- A list of special secondary schools, and contacts.
- What is the history of Kenyatta University?
- Public Universities in Kenya
- Best Public High Schools in Kiambu County.