Osteomyelitis is also termed a bone infection. This is an inflammation of the bone from an infection. Not only does it affects the spine, arms but also the legs. Infection can reach the bone through the bloodstream or infection of nearby tissues. At times infections may start in the bone itself when exposed to germs. Those at risk are:
- Smokers.
- Those with chronic conditions e.g. kidney failure.
Symptoms.
- Fever.
- Fatigue.
- Pain in the regions/areas of infection.
- Swelling and redness in the infected areas.
Causes of osteomyelitis
Staphylococcus bacteria is the common cause of osteomyelitis. The germs may be found in the nose or skin of healthy individuals. Germs can enter the bone through:
- Injuries. Broken bones that are severe stick out through the skin. Such injury allows germs to enter the bone.
- Surgery- In the replacement of fractures or surgeries to replace joints direct contamination can occur.
- Bloodstream infections such as pneumonia. Germs travel from the lungs through the bloodstream to the weekend areas of the bones.
Risk factors
- Age- as one gets older their immune system lessens.
- Orthopedic surgery or recent injury such, as a nail wound. They act as pathways for infection.
- Use illicit drugs. At times there is no use of sterile needles or even disinfection of skin before injections.
- Conditions that suppress the immune system e.g. cancer treatment or poorly controlled diabetes.
- Use of catheters and intravenous lines in conditions like dialysis machine tubing.
- Circulation disorders- make fighting small infections difficult as the body is not able to transport infection-fighting cells to the needed areas. Diseases that can impair blood circulation are sickle cell disease, poorly controlled diabetes, and peripheral artery disease.
Complications of Osteomyelitis
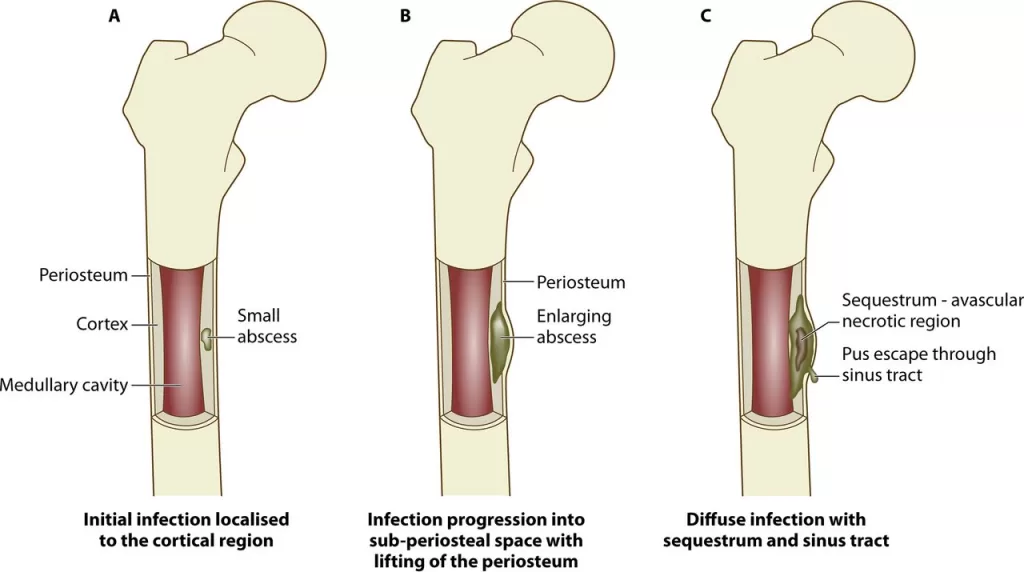
- Septic arthritis- where infection spread to joints.
- Skin cancer. The risk of developing squamous cell cancer is high due to an open sore from osteomyelitis that starts draining pus.
- Impaired growth in children when the growth plates are infected. These are softer areas at the ends of the long bones in the arms and legs.
- Osteonecrosis or bone death occurs when there is no blood circulation in the bone.
Prevention
- Avoid cuts, animal scratches, and bites.
- Clean injuries and cover them with a clean bandage.
Diagnosis of Osteomyelitis
- Physical examination. The affected bone is examined for any tenderness plus swelling.
- Blood test e.g. a full blood count and C-reactive protein. These can indicate the germs responsible for the infection.
- Imaging test:
- X-rays to reveal any damage to the bone.
- MRI produces a detailed image of bones and tissues.
- A CT scan creates a detailed cross-sectional view of one’s internal structures.
- Biopsy. Bone biopsy shows the type of germs causing the infection. This helps in treatment.
Treatment
- Use of medication. Chronic medical conditions e.g. diabetes can be managed through the use of medicine. Antibiotics used depend on the type of germs causing the infection.
- No smoking.
- Surgery. It depends on the severity of the infection. Types of surgery procedures are:
- Removal of the diseased bone and tissues. Done in a procedure known as debridement.
- Draining of pus/ any fluid in the affected areas.
- Removal of foreign objects e.g. screws from previous surgeries.
- Restoration of blood flow by debridement. Helps the body to repair damaged blood vessels and the formation of new bones.
- Amputations of limbs in the affected areas to stop the spread of infections.
- Egerton university, fees, location, courses.
- Kenya Institute of special education, courses.
- The best private primary schools in Nyeri county.
- Bay head elementary school history, enrolment, programs offered.
- What is the history of Kenyatta University?
- List of best private primary schools in Kirinyaga County.
- A list of special secondary schools, and contacts.