Arthritis is the swelling and tenderness of joints in the body. Joints are areas where bones meet and are moveable. There are made of soft tissues that prevent bones from rubbing against each other. Areas mostly affected by arthritis are the feet, hands, hips, knees, and lower back.
Types of arthritis
- Gout– Too much uric acid in blood forms uric acid crystals in the joints.
- Rheumatoid– This is where the immune system attacks the synovial membranes in the joints making them swell.
- Osteoarthritis– This occurs as a result of too much pressure on joint cartilage leading to bones grinding directly into each other. It is the most common type of arthritis.
- Ankylosing spondylitis – It affects mostly the lower back (spine).
- Juvenile– The immune system attacks tissues around the joints. It mostly affects children.
- Psoriatic– The immune system attacks its own tissues due to an autoimmune condition.
Causes Arthritis
So, this illness has no specific cause, but there are factors that may lead one to develop arthritis. These include:
- Family history
- Career choice or sports activity especially those that put too much stress on joints.
- Age – The older the high risk to develop arthritis
- Weight – Obesity can lead to arthritis due to strain on the joints.
- Lifestyle – Smoking can lead to arthritis.
- Gender – Females are at a higher risk than males
Symptoms of arthritis
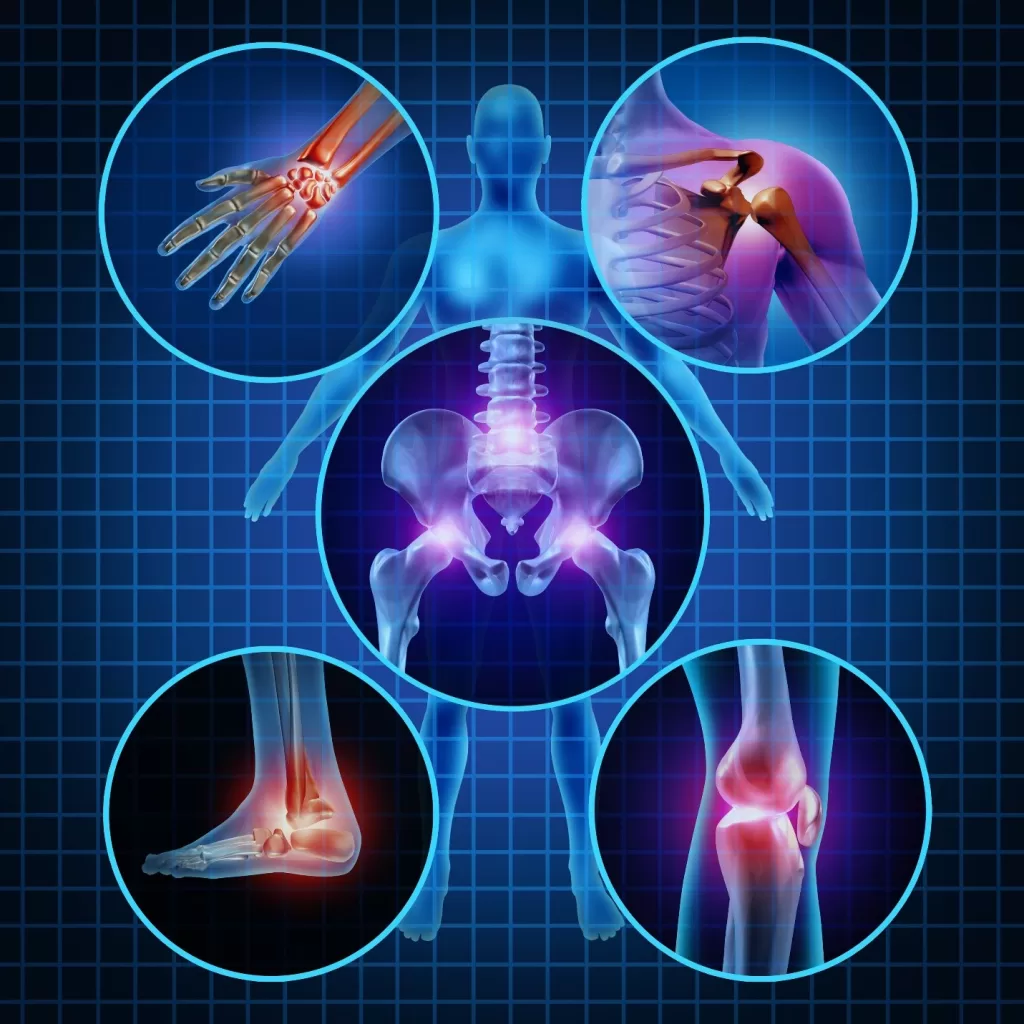
Each type has different symptoms ranging from mild to severe. The most common symptoms are;
- Joint pains.
- Swelling.
- Tenderness.
- Redness.
- Stiffness.
Diagnosis
Physical examination – To assess the mobility of joints, check for swelling and tenderness.
Imaging examination – X-ray and MRI revealed a bone fracture and tissue inflammation.
Blood test – uric acid test can detect gout. The rheumatoid factor test detects inflammatory proteins that cause rheumatoid.
Prevention
- Maintaining a healthy body weight.
- Avoid tobacco products.
- Reducing risks that can lead to joint injuries.
Treatment
So, there is no cure for this illness. However, there is a treatment that helps manage the pain depending on the severity and symptoms. Treatment includes:
- Paul Rudd age, wife, children, comedies and films, worth.
- Noelle Dunphy age, origin, harassment, career, net worth.
- Bernie Sanders age, family, wife, children, career, net worth.
- Rick Williams Bio- Age, Education, Wife, Children, and Career
- Melissa Adan NBC7-KNSD, Age, Children, Husband, Net Worth.
- Who is Ida Odinga Age, Education, origin, Career?
- Scott Fisher wiki, age, KTBC-7, family, children, wife, net worth.
- Medication – Anti-inflammatory and pain relievers make the symptoms manageable.
- Physical therapy – Helps improve the strength of joints.
- Therapeutic injections – Cortisone shots relieve pain and inflamed joints.
- Massage – Applying light pressure on affected areas increases blood flow and relieves pain.
- What is the history of Kenyatta University?
- Mount Kenya University history, fees, courses
- Public Universities in Kenya
- How is The Lenana Boy school and location?
- A list of special secondary schools, and contacts.
- Bay head elementary school history, enrolment, programs offered.
- Best Public High Schools in Kiambu County.