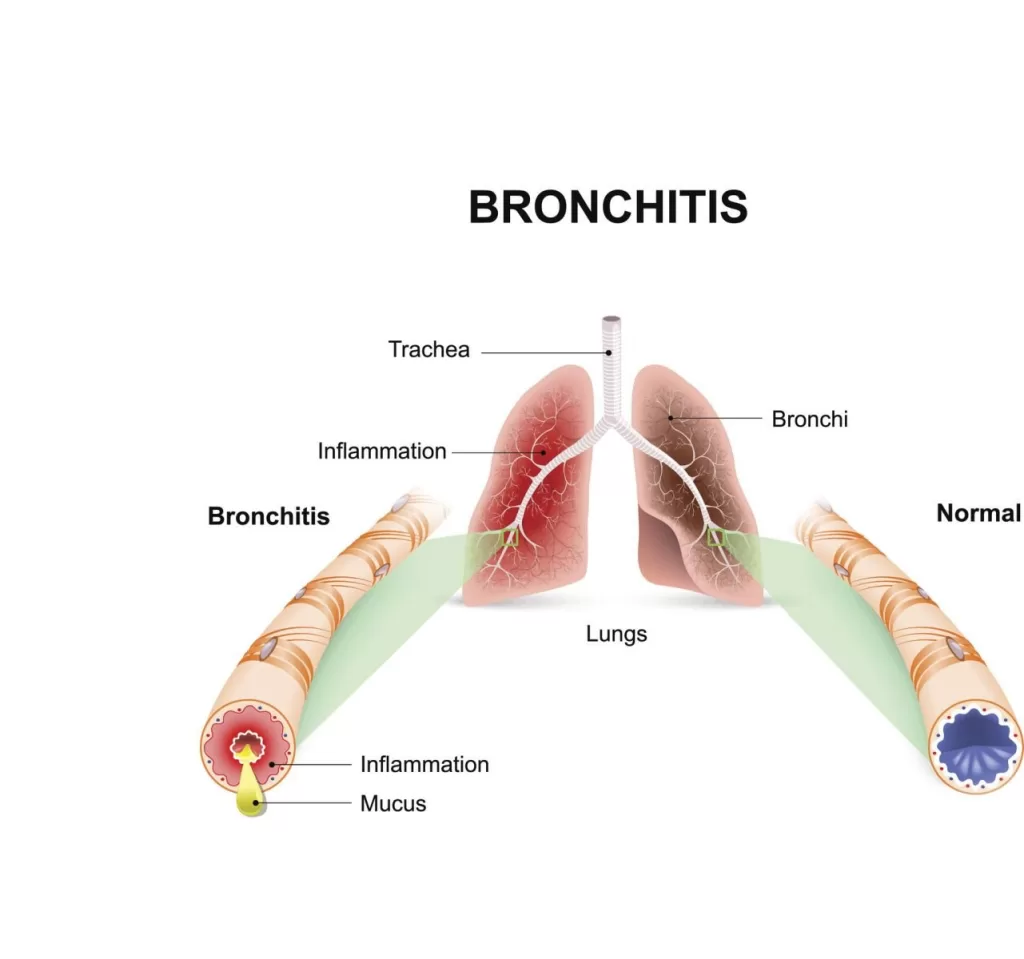
Bronchiolitis is a common infection of the lungs, that mostly affects infants and children. Causes irritation, swelling, and mucus build-up in the lungs (small airways known as the bronchioles). However, it is caused by a virus whose onset symptoms are similar to a common cold. Some children experience coughing, wheezing, and trouble when breathing. Affects children below 2 years of age, whose lungs are not fully developed and whose ability to fight infection is low.
Cause.
So, bronchioles are the smallest airway in the lungs. One is infected when a virus enters the bronchioles. Making them become irritated and swollen. Therefore, breathing is difficult from mucus buildup in the airways. It occurs in cold and rainy periods. Viruses are easily spread from one person to the next through:
- Droplets are released into the air when one sneezes, coughs, or talks.
- Touching infected objects e.g. door knobs, or toys after which one touches the eyes, nose, or mouth.
Viruses that cause bronchiolitis are:
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
- Viruses that cause common cold infection e.g Influenza.
Symptoms of bronchiolitis
- Runny nose.
- Cough.
- Fever.
- Wheezing.
Also, severe symptoms include:
- Poor feeding.
- Being sluggish.
- Blue lips, fingertips, or toes.
- Struggling to breathe, cry, or speak.
- Breathing very fast.
Risk factors.
- Premature birth.
- Lung/heart conditions.
- Weakened immune system.
- Cross transmission.
- When surrounded by smokers.
- Being in overcrowded places.
Complications of bronchiolitis
- Low oxygen levels in the body.
- Respiratory failure.
- Also, dehydration from not taking enough fluids.
- Pauses breathing mostly in babies born prematurely.
Prevention
- Limit contact with the sick.
- Clean and disinfect surfaces e.g. toys and door knobs.
- Washing of hands before holding infants.
- Cover nose and mouth if one needs to cough or sneeze.
- Breastfeeding of babies is important as milk contains antibodies that help fight infections.
- Use of face masks.
- Vaccination.
Diagnosis of bronchiolitis
- Physical examination where the doctor listens to the lung by use of a stethoscope.
- Chest x-ray to check for infections in the lungs e.g. pneumonia.
- Blood tests like full blood count can show an increase in the white blood cell count in the presence of an infection.
- Viral testing. The nose is gently swabbed and tested.
Treatment.
- Use of nebulized albuterol treatment where a fine mist of medicine is created by the machine and taken to the lungs.
- Ging antibiotics that treat bacterial infections.
Home remedies.
- Humidifying the air- dry air may be moisturized by a vaporizer. Helps to loosen mucus and lessen the cough. Humidifiers should be clean always to prevent the growth of bacteria and molds.
- Giving fluids to hydrate-Those that are 6 months and below are to be breastfed or given formula. Those over 6 months can either drink milk, water, and juice
- Saline nasal drops- are safe, and effective and do not cause irritation to the nose.
- Use of pain relievers e.g. ibuprofen to ease symptoms.
- Also, avoid smoking. Smoke makes respiratory infection symptoms to worsen. If it’s a must to smoke it should be away from infants.
- What is the history of Kenyatta University?
- Egerton university, fees, location, courses.
- List of Best private secondary schools in Nairobi County.
- List of Accredited Private Universities in Kenya
- Kenya Institute of special education, courses.
- Public Universities in Kenya
- A list of special secondary schools, and contacts.