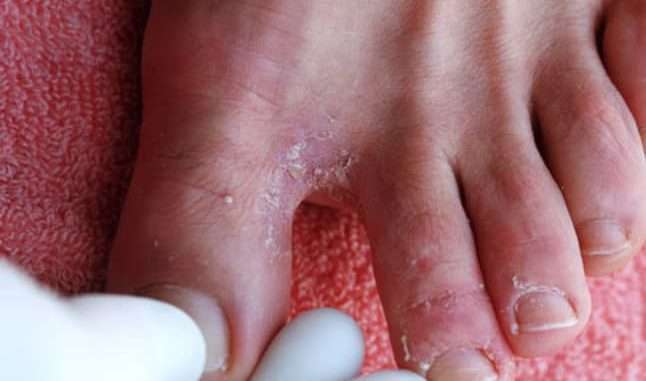
An athlete’s foot is a fungal infection that occurs between toes. It is a form of ringworm. It spreads through contaminated floors or even towels. Therefore, it is very contagious. In addition, it mostly occurs in sweaty feet. It makes the skin appear raw and red. Sometimes, this infection makes the feet smell bad.
Types of Athlete’s Foot.
1.Toe web Infection.
This is the most common type. It affects the skin between the fourth toe and the last toe.
2.Vesicular type Infection.
This type of infection appears at the bottom of the feet. It features blisters that have fluid.
3.Mocassin type Infection.
This type of infection affects the bottom of the feet and the edges of the feet. In some cases, the infection affects the toenails. The skin at the bottom of the feet thickens and cracks.
4.Ulcerative Infection.
This is the rarest type of infection. Open wounds appear between the toes. The wounds may also appear at the bottom of the toes.
Symptoms.
- Cracked skin between the toes.
- Itchiness especially after taking off shoes and socks.
- Blisters.
- Dry skin.
- Swollen skin that appears red or gray.
- Burning.
What causes Athlete’s Foot?
Athlete’s foot spreads through skin-to-skin contact. It spreads in areas that have large groups of people. Moreover, one can also get an athlete’s foot by sharing towels, beddings, and socks with someone who already has the infection.
However, the main cause of the athlete’s foot is fungi. The fungi live in warm and moist environments. Therefore, the fungi feed on the skin and toenails. However, walking barefoot also increases the chances of having an athlete’s foot.
- Randy Meier Bio-Age, Edu, Children, Wife, Net Worth.
- Alexis Rivas KNSD, age, family, children, husband, net worth.
- Laurie Metcalf Biography, Age, Husband, Children, Lesbian, and TV Shows
- Burna Boy bio-age, family, wife, children, music career.
- James Menendez Bio, Wiki, BBC London, Age, Education, Height, Family, Wife, Children, and Career
- Matt Damon age, education, wife, children, career.
- Russ Spencer age, education, children, wife, net worth, and fox5.
People who are at risk of having athlete’s foot are those with;
- Diabetes.
- Obesity.
- Wounds on the feet
- A weak immune system.
Diagnosis.
A doctor can diagnose by just checking the feet and having a review of the symptoms. In addition, the doctor may also remove a small part of the skin and examine it in the laboratory. Fungal cells are visible when potassium hydroxide solution dissolves in the skin cells.
However, an athlete’s foot barely goes away if it is not treated. It may spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment.
Antifungal creams treat athletes’ feet. Sprays, Oils, and powders also work effectively. Therefore, it is important to finish the full prescription. This is to avoid the infection coming back and it may be hard to treat it.
Prevention.
The following are measures that can help prevent the infection.
- Washing the feet daily.
- Avoid sharing towels, socks and beddings.
- Wearing different pairs of shoes.
- Changing socks regularly.
- Let the feet air out as much as possible.
- Keep the feet dry and cool.
- Avoid swimming pool and public baths.
So, an athlete’s foot is a fungus that can easily be treated.
- Public Universities in Kenya
- Mount Kenya University history, fees, courses
- How is The Lenana Boy school and location?
- List of Accredited Private Universities in Kenya
- Kenya Medical Training College, courses, requirements.
- Bay head elementary school history, enrolment, programs offered.
- List of best private primary schools in Kirinyaga County.