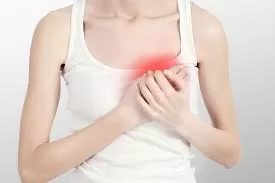
Mastitis in humans is the painful inflammation of breast tissue that results in pain, swelling, and redness of the breast. Mastitis commonly affects breastfeeding mothers. Therefore, when one suffers from mastitis, it is advisable for breastfeeding mother not to stop feeding their child as it helps the infection to clear faster. Breast milk also has antibacterial properties that help the body fight infections.
Causes of mastitis in humans
- Having breast implants.
- When milk is trapped in the breast for long.
- A blocked milk duct may lead to milk backup in the breast.
- Bacteria invasion into the breast through cracks on the nipples or through the milk duct opening.
Symptoms.
- Breast tenderness on touching.
- Swelling of the breast.
- One may have breast lumps.
- Burning sensations.
- Fever.
Risk factors of mastitis in humans
- Improper nursing methods.
- Poor nutrition.
- Smoking.
- Wearing tight-fitting bras that restrict milk flow.
- Previous bout of mastitis while breastfeeding.
- Having cracked nipples.
Complications.
- Mastitis can lead to a collection of abscesses in the breast.
Prevention.
- During feeding ensure the baby latches on properly.
- Before switching the baby from one breast ensure they have completely emptied it.
- Drain milk from the breast while breastfeeding.
- No smoking during the nursing period.
- Ensure there are proper hygiene methods such as handwashing.
- Prevent moisture from accumulating in the breast pad/bras.
- Drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration.
Home remedies for mastitis in humans
- Use of ice pack to reduce swelling of the breast.
- Use of pain relievers such as ibuprofen.
- Lymphatic drainage- gently apply light pressure to the breast towards the lymph nodes. This reduces swelling by moving the fluid in the breast.
- Reverse pressure softening massage. It reduces swelling in the areola and the nipple by moving the fluid away from it. Allows the baby to latch more easily to the breast.
- Wearing a supportive bra that does not put pressure on the breast.
Diagnosis.
- Physical examination.
- Breast ultrasound.
- Breast biopsy.
Treatment.
- Use of antibiotics.
- Pain relievers.
- Kenya Institute of special education, courses.
- List of best private primary schools in Kirinyaga County.
- Public Universities in Kenya
- Egerton university, fees, location, courses.
- Bay head elementary school history, enrolment, programs offered.
- What is the history of Kenyatta University?
- Best Public High Schools in Kiambu County.