Bedsores are injuries or wounds to the skin and the underlying tissues as a result of prolonged pressure on the skin. Mostly affects people who are immobile for long periods of time e.g;
- Those in wheelchairs.
- Bedridden may be due to a coma.
- Those with prosthetic devices.
Bedsores develop on parts where bones sit closest to your skin, such as :
- Elbows.
- Heels.
- Hips.
- Back.
- Buttocks.
- The tailbone.
These wounds can develop into large, deep wounds thus leading to infection when not treated. Other names used to refer to bedsores are:
- Pressure sores.
- Pressure ulcers.
- Pressure wounds.
- Pressure injuries.
- Decubitus ulcers.
The following are disease conditions likely to increase the risk of one developing bedsores;
- Diabetes.
- Heart failure.
- Kidney failure.
- Malnutrition.
- Cancer.
- Dementia.
- Spinal cord injury.
Causes of bedsores
Bedsores occur when there is pressure on the skin layer known as the epidermis leading to a lack of blood supply. Contributing factors for bedsores are:
- Pressure- blood carries oxygen and nutrients to tissues, thus when there is constant pressure on any body part it leads to less blood flow. Failure of blood flow leads to damage/death of tissues, especially areas that have no muscles or fat layer e.g. tailbone and shoulders.
- Friction- when fragile skin rubs against clothes or bedding it makes it vulnerable to injury.
- Stretching of the skin due to two surfaces moving in the opposite direction. This can be due to sliding down in an inclined position e.g. from a bed.
Stages of bedsores
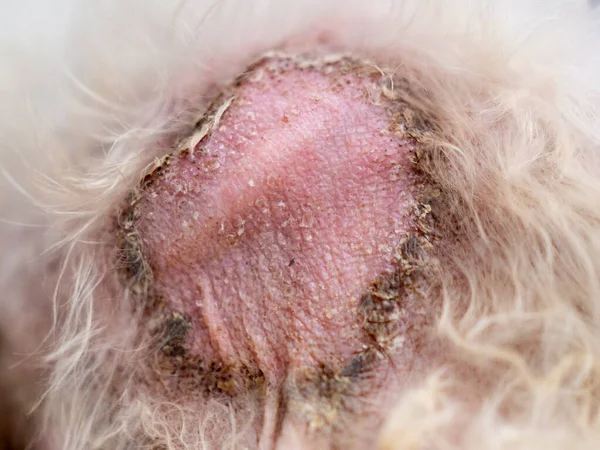
- Stage 1- For light-skinned individuals the skin may appear to be red/pinkish and tender on touching.
- Stage 2 – a blister-like wound is seen on the skin.
- Stage 3 – a wound that is noticeable, on to the skin’s fatty layer.
- Stage 4 – wounds can penetrate all three layers of the skin thus exposing the muscles, tendons, and bones.
Symptoms of bedsores
- Fever plus chills.
- Oozing of pus.
- Pain to the areas surrounding the wound.
- Swelling.
- The wound has a foul smell.
Risk factors.
- With exposure to stool and urine, the skin is more vulnerable.
- Immobility results in poor health or spinal injury.
- Poor nutrition and hydration – diet should have proteins, vitamins, and minerals without forgetting fluids so as to maintain healthy skin.
- Lack of sensory perception especially when one has spinal cord injuries, can lead to one not being aware of the warning signs to change in position.
- Medical conditions affecting blood flow e.g. vascular disease increases the risk of tissue damage.
Complications of bedsores
- Bone and joint infections- joint infections damage cartilage plus tissues while bone infection reduces joint and limb functions.
- Non-healing wounds can develop into a type of squamous cell carcinoma if treatment is not given in time.
- Can lead to sepsis.
- Cellulitis where the skin infection can also affect the connected soft tissues. This can lead to inflammation and swelling of the affected areas.
Prevention.
- Proper skin care routine e.g. ensuring the skin is clean and dry.
- Doing exercises daily.
- Repositioning to avoid stress on the skin.
- Eating a balanced nutritional and fluid intake.
- No smoking.
Treatment.
- Cleaning and dressing of wounds so as to prevent contamination by covering them with bandages.
- Use of pain relivers e.g ibuprofen.
- Damaged tissues should be removed.
- Use of surgery to treat large bedsores that fail to heal.
- Giving palliative care to the sick as it helps to reduce stress thus increasing recovery.
- Reducing pressure on affected areas by repositioning the sick.
- List of Accredited Private Universities in Kenya
- List of best private primary schools in Kirinyaga County.
- Mount Kenya University history, fees, courses
- Kenya Institute of special education, courses.
- List of Best private secondary schools in Nairobi County.
- Best Public High Schools in Kiambu County.
- What is the history of Kenyatta University?