Mumps is an infection that affects the salivary glands. It causes swelling of one of the glands. Mumps outbreaks are common in the United States. These cases mostly occur in unvaccinated people in places such as schools and other public surroundings.
Signs And Symptoms
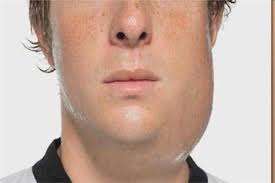
People infected with the virus show few or no signs. Signs and symptoms start developing after two to three weeks after contracting the virus. The signs and symptoms include the following
- Increased pain in the salivary glands.
Normally a person experiences some sharp pain in the swollen salivary glands.
- Increased pain while swallowing.
When a person feels pain while swallowing food or chewing this could be an alarm to visit a doctor for screening.
- Fever
An increase in body temperature can also be a sign of the mumps virus. This causes discomfort. A person experiences too much sweating and shivering. Regular temperature taking to check fevers is advisable.
- Lack of appetite
When a person has a loss of appetite it is considered to be a symptom of mumps. This happens when a person has a decreased need to eat. This also applies to a person’s favorite food.
- Increased fatigue
This is increased tiredness after completing the same habits and routines. If a person experiences abnormal tiredness should check for mumps.
- Carly Cassady bio-age, family, children, net, husband, career.
- Who is Natalee Holloway, family, siblings, disappearance?
- Ed Sheeran bio-age, education, marriage, career, net worth, songs.
- Ashley Johnson bio, Age, family, career, net worth.
- Franklin Mithika Linturi bio-age, wife, origin.
- Jason Statham Bio-age, early life, family, net worth.
- Katie Orth Bio, Age, Edu, Family, Children, Net Worth.
Causes of Mumps.
A virus that can be transmitted easily among people is the main cause of mumps through infected saliva. An immune person has a lower chance of contracting mumps as compared to a non-immune person. A non-immune person can contract saliva and mucus droplets from an infected person after sneezing or coughing. Utensil sharing among people with mumps can also be a cause of mumps.
Treatment of Mumps.
The best prevention of mumps is vaccination. There are two recommended doses of mump vaccine. The first dose should be administered to children between the age of 12 and 15 months while the second should be given at the ages of 4 and 6 years. International travelers and healthcare workers are also advised to take the two doses of vaccines. However, some of the people that are not advised to take the vaccines are
- People who are allergic to the antibiotic neomycin
- Expectant women or women who are planning to conceive within a period of a month.
- People with complicated immune systems.
Those who should wait to get the vaccine include
- An ill person where he/she should wait till recovery.
- A pregnant woman. She should wait till she has given birth.
Some of the side effects of the vaccine include
- Mild fever
- Achy joints.
- What is the history of Kenyatta University?
- Best Public High Schools in Kiambu County.
- How is The Lenana Boy school and location?
- Public Universities in Kenya
- List of Best private secondary schools in Nairobi County.
- The best private primary schools in Nyeri county.
- List of Accredited Private Universities in Kenya