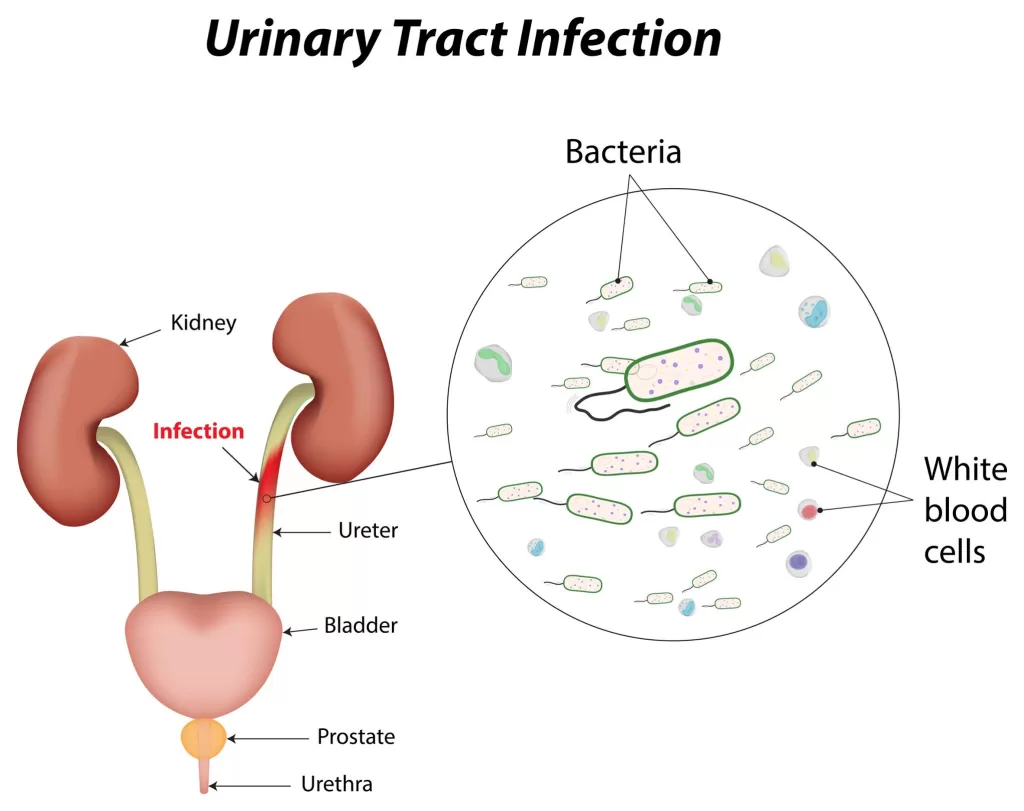
Urinary Tract Infection( UTI) is a bacterial infection that affects parts of the urinary system. The urinary system is made up of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. So, in most cases, UTI affects the lower part of the urinary tract which is the bladder and the urethra.
Cause.
The Escherichia coli (E.coli) bacteria is the known cause of UTI. The infection occurs when the bacteria enter the urinary tract and spreads.
Risk factors for Urinary Tract Infection
- Body anatomy– Females are more easily affected by UTI than males as the urethra is next to the rectum. E.coli is common in the gastrointestinal tract thus it can get into the urethra from the anus when body hygiene is poor.
- Specific birth controls – For instance, diaphragms increase the risk of UTI.
- Sexual activity- So, those that are sexually active have a high risk.
- Menopause – A decline in the circulating estrogen makes females more susceptible.
- Catheter use- Hospitalized persons are at risk as catheter use can easily introduce bacteria to the bladder.
- Babies born with urinary tract problems have trouble when passing out urine. Retention of urine in the urethra easily causes UTI.
- Recent urinary procedures where medical equipment being used in the urinary tract may lead to UTIs if not properly sterilized.
Symptoms for Urinary Tract Infection
- Pain when passing urine.
- Back and pelvic pain.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Lower belly discomfort.
- Sometimes there may be blood in the urine.
- Discharge that makes the urine look cloudy.
- Nause and vomiting.
- Fever.
How to Prevent Urinary Tract Infection
- Drink plenty of fluids e.g water as it helps dilute the urine. One also tends to flush out the bacteria when one urinates.
- Improve personal hygiene- females should wipe from front to back after a bowel movement to prevent bacteria in the anus from entering the urethra.
- Change of birth control method e.g un-lubricated condoms as they contribute to bacterial growth.
- Empty the bladder soon after having sex, these help to flush out bacteria.
- Avoid the use of irritating products like sprays and soap in the genital areas as they kill the normal flora in the urethra thus making one more susceptible to bacteria.
Diagnosis for Urinary Tract Infection
- Urinalysis- in the urine sample look for bacteria, white blood cells, and red blood cells.
- Culture- helps to tell the strain causing the infection and the best treatment to give.
- Ultrasound- shows if there is any abnormality in the urinary tract organs.
- A cystoscopy-a small camera device is inserted into the bladder. At the time a small piece of the bladder is removed and tested to rule out bladder inflammation.
Treatment.
However, UTI is treated by the use of antibiotics.
- How is The Lenana Boy school and location?
- Kenya Medical Training College, courses, requirements.
- List of Accredited Private Universities in Kenya
- Egerton university, fees, location, courses.
- What is the history of Kenyatta University?
- List of best private primary schools in Kirinyaga County.
- A list of special secondary schools, and contacts.