Streptococcal infection is caused by one of the many species of Streptococcus. The gram-positive, sphere-shaped bacteria or coccal brings about several disorders. These include strep throat, pneumonia, wound, and bloodstream infections. Each group of these bacteria spread in different ways. For instance, through coughing or sneezing. Moreover, coming into contact with infected wounds or sores, or from mother to infant when giving birth. The infection affects several body parts such as the throat, sinuses, middle ear, lungs, skin, heart valves, the tissue under your skin, and the bloodstream.
Symptoms
- Red, painful swollen tissues.
- Scabby sores.
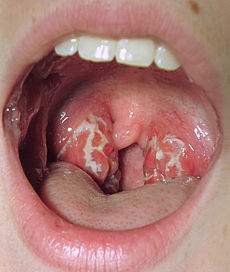
- Sore or throat.
- Rashes on the affected area.
- Scarlet fever with swollen glands about 12 to 48 hours after infection.
- Impetigo results in sores on your skin that form blisters that may burst, leaving a moist area with a yellow-brown crust at its edge.
- Pain while swallowing.
Types of Streptococcal infection
The groups are given based on the appearance, and chemical components when grown in a lab. These groups are;
- Group A streptococci -These are bacterias that are commonly found in your throat and skin. Several people may be carriers of this infection and show no symptoms.
- Group B-Group B strep- This is bacteria that is commonly found in your intestines or in the lower genital tract. It is known to be harmless in healthy adults. However, in newborns, it may result in a more serious illness by the name group B strep. This infection is also risky in adults who suffer from certain chronic conditions for instance diabetes and liver disease.
- Viridans- This is a word used for five groups of Streptococci which include Streptococcus anginosus, sanguinis, mitis, salivarius, and mutans. Each group had about 30 species that may result in illnesses in human beings.
- Group D- These are found in the gastrointestinal tracts of human beings and animals.
Treatment of Streptococcal infection
Antibiotics mostly penicillin is common in treating this illness. F
or necrotizing fasciitis, some surgery is done to remove the dead tissue.
Strep throat mostly takes one to two weeks to heal even with no treatment. However, antibiotics shorten the incubation period. Again, they help prevent the spreading of the infection to other body parts and, also to other people. Moreover, they help to prevent rheumatic fever, although kidney inflammation may not be prevented. So, you do not need to start taking antibiotics immediately. It is advisable to give it at least 1 to 2 days for culture results to show. But, in case a family member suffers of had suffered rheumatic fever, this case should be different. In this case, every streptococcal sign in any member must be treated as soon as it is detected.
- Kenya Institute of special education, courses.
- Best Public High Schools in Kiambu County.
- Bay head elementary school history, enrolment, programs offered.
- What is the history of Kenyatta University?
- List of Best private secondary schools in Nairobi County.
- Kenya Medical Training College, courses, requirements.
- The best private primary schools in Nyeri county.