Diphtheria which is pronounced as( dif-theer-e-uh) is a bacterial infection that affects parts of the nose and throat. Due to its widespread vaccination, few cases are reported in developed countries but a high number of cases in developing countries. However, there is a treatment for diphtheria in its early stages. In its advanced stages, it causes damage to the heart and kidneys. It can be a cause of death mostly in babies.
It is mostly known to be a highly transferable disease. The infected people develop problems such as breathing and swallowing. Additionally, sores may begin to appear on their skin. This disease mainly affects those living in unhealthy and crowded places.
Causes of diphtheria.
A bacterium known as Corynebacterium diphtheriae is the main cause of diphtheria. It leads to breathing and swallowing problems due to toxin release that builds up grey tissue in the throat. An infected person develops skin sores that do not cure in hotter areas. This type is known as cutaneous diphtheria. It spreads through sneezing or coughing by an infected person. In addition, one may contract it through getting into contact with infected person items.
Signs and symptoms of diphtheria.
The signs develop between the second and fifth days of infection. The signs include the following
- Mucus flow from the nose.
- Breathing difficulties.
- Pain in the throat especially when swallowing.
- Swelling of the glands.
- High body temperatures.
Complications of diphtheria.
The following problems are brought about by untreated diphtheria
- Difficulties in breathing due to producing a toxin that damages nose and throat tissues.
- Heart damage spread into the bloodstream causing problems such as swelling of the heart muscles.
- Nerve damage leads to difficulty in swallowing and also swelling.
Treatment and prevention.
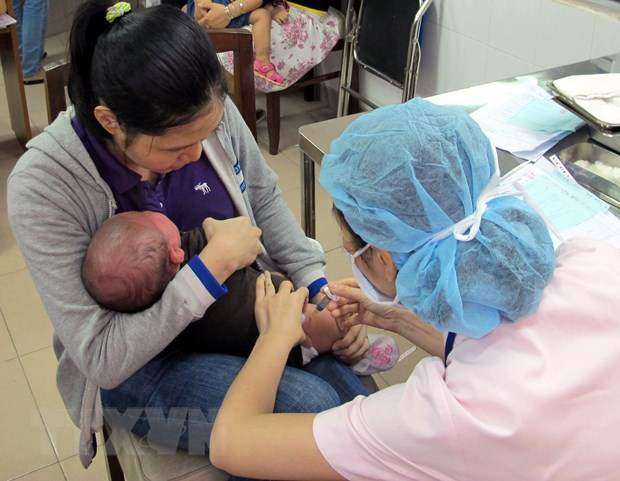
Vaccination is the primary prevention method of diphtheria. The vaccination is available for both children and adults. It is made up of five injections which are given to children between the ages between two months and six years. However, some of the side effects related to the vaccine include sleepiness and high body temperatures. Booster shots are also available in order to increase the resistance to the disease getting into the body.
- Mike Lindell age, wife, children, current life, net worth.
- Amanda Ruiz Bio, Wiki, Age, KTBC -7, Education, Family, Children, Husband, Net Worth
- Colleen Williams NBC4-KNBC, Age, Children, Wife, Net Worth.
- Todd Strain Bio, Wiki, NBC7-KNSD, Age, Education, Family, Children, Wife, Net Worth, and Career
- Justin Cheung age, wife, children, movies, career, net worth.
- Cory James Bio, Wiki, DC News Now, Age, Education, Family, Children, Wife, Net Worth, and Career
- Dwayne Johnson Bio, Age, Edu, family, Movies, Net Worth
- The best private primary schools in Nyeri county.
- What is the history of Kenyatta University?
- Best Public High Schools in Kiambu County.
- List of Best private secondary schools in Nairobi County.
- Kenya Institute of special education, courses.
- How is The Lenana Boy school and location?
- Kenya Medical Training College, courses, requirements.